(UPSC Economics Optional 2014) Question 4:
What do you mean by existence and uniqueness of equilibrium in a market? Examine these concepts in a market where both demand and supply curves are downward sloping.Existence of an equilibrium:
An equilibrium 'exists' when at a certain positive price the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. Qd = Qs. At such a price there is neither excess demand not excess supply. ( derived from Walrasian equilibrium concept)
Uniqueness of an equlibrium:
Uniqueness of an equlibrium is related to the slope of the excess demand function that is the curve that shows the difference between the Qd and Qs at any one price.
Take Excess demand as E(pi) = Qd(pi) - Qs(pi), E(pi) should intersect the vertical price axis to have a unique and stable equilibrium.
When both demand and supply curves are downward sloping:
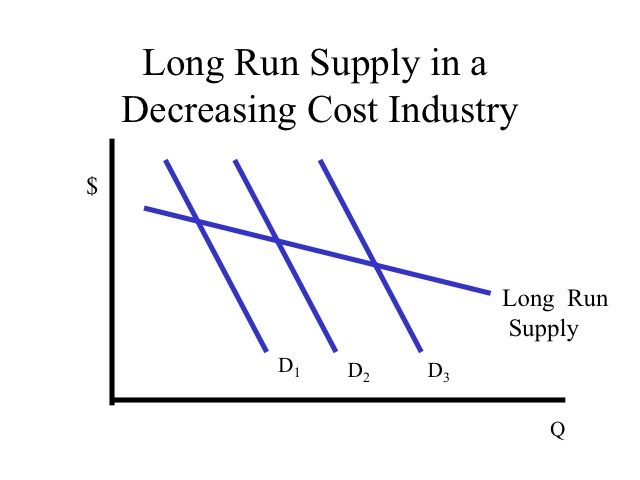
This is seen in long-run supply curve in a decreasing cost industry. When both the demand curve and the supply curve are downward-sloping, it is possible for them to have more than one point of intersection. For simplicity, we assume a situation where the supply curve is downward-sloping but is flatter (more horizontal) than the demand curve. In this case, there is a unique point of intersection of the curves and this gives the market price and equilibrium quantity traded.
Source: Refer this Link and Wiki
No comments:
Post a Comment